Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 33
ADVERTISEMENT
515
13.4 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Green Decaf Coffee
S
T
PECIAL
OPIC 13.2
Caffeine, the primary stimulant found naturally in
and pressure. It penetrates the beans more than a typical
coffee, tea, and chocolate, is artificially added to many
liquid would, and then, like a liquid, dissolves the
other products, such as soft drinks, over the counter
caffeine. When the supercritical carbon dioxide is later
stimulants, cold remedies, and pain relievers. It is the
separated from the beans, it carries about 97% of the
world’s most widely used drug. Different types of coffee
caffeine along with it. Any residue of carbon dioxide
contain different amounts of caffeine, and different
remaining on the beans is quickly lost as gaseous CO
.
2
brewing techniques lead to further variations in content.
The workers employed in this method of decaffeination
Depending on the type of coffee (an arabica coffee
are safer without the contact with dichloromethane, and
contains about half the caffeine of a robusta) and the
the coffee drinkers do not have to worry about the very
fineness of the grounds, the drip method of brewing
slight residue of dichloromethane that remains when the
leads to 110 to 150 mg of caffeine per cup. Instant
coffee is decaffeinated using the direct-contact method.
coffee has 40-108 mg of caffeine per cup.
The average cup of coffee contains from 40
to 150 mg of caffeine.
Some people like the taste of coffee and
the rituals associated with it (the customary
cup of coffee after dinner) but do not like
the effects of the caffeine. They may choose
to drink decaffeinated coffee, which has 2-4
mg of caffeine per cup. A coffee must have
at least 97% of its caffeine removed to be
considered decaffeinated coffee.
One of the commercial methods for
decaffeinating coffee is the direct-contact method. The
unroasted coffee beans are first softened with
steam and then brought in direct contact with
a decaffeinating agent, such as dichloromethane
(most often called methylene chloride in
this context), CH
Cl
. The caffeine dissolves
2
2
in the dichloromethane, after which the
dichloromethane/caffeine solution is removed
from the beans.
There is some evidence that dichloromethane is
carcinogenic. According to the United States Food
and Drug administration (FDA), most
decaffeinated coffee has less than 0.1
parts per million (ppm) of residual
dichloromethane, which is 100 times
less than the maximum level of 10 ppm
allowed by the FDA. Despite this low
residual concentration of dichloromethane,
there is still some concern about a possible health
hazard, so substitutes are being sought for many of its
applications.
One alternative to the current methods of
decaffeination uses supercritical carbon dioxide.
The unroasted beans are softened by steam and then
All of these products contain caffeine.
immersed in carbon dioxide at very high temperature
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4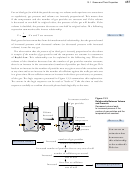 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10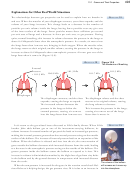 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25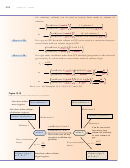 26
26 27
27 28
28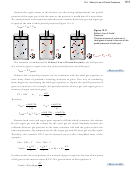 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








