Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
488
Chapter 13
Gases
The Relationship Between Pressure and Temperature
In order to examine the relationship between pressure and temperature, we must adjust
O
10
bjeCtive
b
our demonstration apparatus so that the other two properties (number of gas particles
and volume) are held constant. This can be done by locking the piston so it cannot
move and closing the valve tightly so that no gas leaks in or out (Figure 13.4). When
the temperature of a gas trapped inside the chamber is increased, the measured pressure
increases. When the temperature is decreased, the pressure decreases.
Increased temperature → Increased pressure
O
10
bjeCtive
b
Decreased temperature → Decreased pressure
We can explain the relationship between temperature and pressure using our model
for gas. Increased temperature means increased motion of the particles. If the particles
are moving faster in the container, they will collide with the walls more often and with
greater force per collision. This leads to a greater overall force pushing on the walls and
to a greater force per unit area or pressure (Figure 13.4).
If the gas is behaving like an ideal gas, a doubling of the Kelvin temperature doubles
the pressure. If the temperature decreases to 50% of the original Kelvin temperature,
the pressure decreases to 50% of the original pressure. This relationship can be expressed
by saying that the pressure of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature
of the gas if the volume and the number of gas particles are constant. This relationship is
sometimes called Gay-Lussac’s Law.
P ∝ T if n and V are constant
O
10
bjeCtive
b
Figure 13.4
Constant number
Relationship Between
of gas particles
Temperature and Pressure
Increased temperature leads
Piston locked
Constant volume
to increased pressure if the
in position
number of gas particles and
volume are constant.
Heat added
O
10
Increased temperature
bjeCtive
b
Increased pressure
You can see an
animation that
Increased temperature
demonstrates
this relationship
Increased average velocity of the gas particles
at the textbook’s
Increased number of
Increased force per collision
Web site.
collisions with the walls
Increased total force of collisions
force due to collisions
Increased
area of wall
Increased gas pressure
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4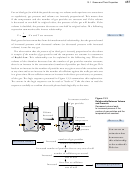 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28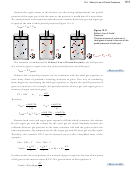 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








