Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
496
Chapter 13
Gases
e
13.1 - Using the Ideal Gas Equation
xample
Incandescent light bulbs “burn out” because their tungsten filament evaporates,
O
15
bjeCtive
weakening the thin wire until it breaks. Argon gas is added inside the bulbs to reduce
the rate of evaporation. (Argon is chosen because, as a noble gas, it will not react with
the components of the bulb, and because it is easy to obtain in significant quantities.
It is the third most abundant element in air.) What is the pressure in atmospheres of
-3
3.4 × 10
moles of argon gas in a 75-mL incandescent light bulb at 20 °C?
Solution
We are given three of the four properties of ideal gases (moles, volume, and temperature),
and we are asked to calculate the fourth (pressure). Therefore, we use the ideal gas
equation to solve this problem.
Step 1 We assign variables to the values that we are given and to the unknown value.
Remember to use Kelvin temperatures in gas calculations.
-3
P = ?
n = 3.4 × 10
V = 75 mL
T = 20 °C + 273.15 = 293 K
mol
Step 2 We pick the appropriate form of the ideal gas equation. Because moles of gas
are mentioned in the problem, we use
PV = nRT
Step 3 We rearrange our equation to isolate the unknown property.
P = nRT
V
Step 4 We plug in the values that are given, including their units. We use the value
for R that contains the unit we want to calculate, atm.
0.082058 L atm
−3
3.4 × 10
293 K
mol
K mol
P =
75 mL
Steps 5 and 6 If the units do not cancel to yield the desired unit, we do the necessary
unit conversions to make them cancel. In this example, we need to convert
75 mL to L so that the volume units cancel. We finish the problem by
calculating the answer and reporting it with the correct significant figures and
with the correct unit.
0.082058 L atm
−3
3.4 × 10
293 K
mol
3
K mol
10
mL
= 1.1 atm
P =
75 mL
1 L
To see a practical application of calculations like Example 13.1, let’s take a closer
look at one of the gas-related issues that Lilia’s sister Rebecca and her coworkers are
dealing with. The apparatus Rebecca is helping to design will be used in the first step
of the commercial process that makes nitric acid for fertilizers. In this step, the gases
ammonia and oxygen are converted into gaseous nitrogen monoxide and water.
(g) + 5O
(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H
4NH
O(g)
3
2
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4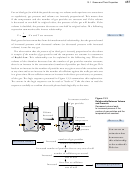 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28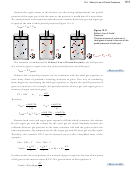 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








