Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 27
ADVERTISEMENT
509
13.4 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
e
13.3 - Equation Stoichiometry
xerCise
Iron is combined with carbon in a series of reactions to form pig iron, which is about
O
19
bjeCtive
4.3% carbon.
2C + O
→ 2CO
2
+ 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO
Fe
O
2
3
2
2CO → C(in iron) + CO
2
Pig iron is easier to shape than pure iron, and the presence of carbon lowers its
melting point from the 1539 °C required to melt pure iron to 1130 °C.
a. In the first reaction, what minimum volume of oxygen at STP is necessary
to convert 125 Mg of carbon to carbon monoxide?
b. In the first reaction, what is the maximum volume of carbon monoxide at
1.05 atm and 35 °C that could form from the conversion of 8.74 × 10
5
L
of oxygen at 0.994 atm and 27 °C?
e
13.4 - Equation Stoichiometry
xerCise
Sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl, found in household bleaches, can be made from a
O
19
bjeCtive
reaction using chlorine gas and aqueous sodium hydroxide:
(g) + 2NaOH(aq) → NaOCl(aq) + NaCl(aq) + H
Cl
O(l )
2
2
What minimum volume of chlorine gas at 101.4 kPa and 18.0 °C must be used to
react with all the sodium hydroxide in 3525 L of 12.5 M NaOH?
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
13.4
Most gaseous systems contain a mixture of gases. Air is a mixture of nitrogen gas,
oxygen gas, xenon gas, carbon dioxide gas, and many others. A typical “neon” light on
a Las Vegas marquee contains argon gas as well as neon. The industrial reaction that
forms nitric acid requires the mixing of ammonia gas and oxygen gas.
When working with a mixture of gases, we are sometimes interested in the total
pressure exerted by all of the gases together, and sometimes we are interested in the
portion of the total pressure that is exerted by only one of the gases in the mixture.
The portion of the total pressure that one gas in a mixture of gases contributes is called
the partial pressure of the gas. Distance runners find it harder to run at high altitudes
because the partial pressure of oxygen in the air they breathe at sea level is about 21
kPa, but at 6000 ft above sea level, it drops to about 17 kPa. Table 13.1 shows the
partial pressures of various gases in dry air. (The percentage of water vapor in air varies
from place to place and day to day.)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4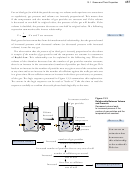 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10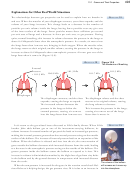 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28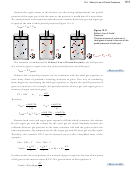 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








