Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
491
13.1 Gases and Their Properties
The Relationship Between Number of Gas Particles and Volume
Figure 13.7 shows how the relationship between the number of gas particles and volume
O
10
bjeCtive
e
can be demonstrated using our apparatus. Temperature is held constant by allowing
heat to move into or out of the system, thus keeping the internal temperature equal
to the constant external temperature. Pressure is held constant by allowing the piston
to move freely to keep the internal pressure equal to the external pressure. When we
increase the number of gas particles in the cylinder by adding gas through the valve on
the left of the apparatus, the piston rises, increasing the volume available to the
gas. If the gas is allowed to escape from the valve, the volume decreases again.
Increased number of gas particles → Increased volume
Decreased number of gas particles → Decreased volume
The explanation for why an increase in the number of gas particles increases
volume starts with the recognition that the increase in the number of gas
particles results in more collisions per second against the walls of the container.
The greater force due to these collisions creates an initial increase in the force
When this person blows more air
per unit area—or gas pressure—acting on the walls. This will cause the piston
into the balloon, the increased
to rise, increasing the gas volume and decreasing the pressure until the internal
number of gas particles initially
and external pressure are once again equal (Figure 13.7). Take a minute or two
leads to an increased pressure.
to work out a similar series of steps to explain why decreased number of gas
Because the internal pressure is
now greater than the pressure
particles leads to decreased volume.
of the air outside the balloon,
The relationship between moles of an ideal gas and volume is summarized
the balloon expands to a larger
by Avogadro’s Law, which states that the volume and the number of gas particles
volume.
are directly proportional if the temperature and pressure are constant.
V ∝ n if T and P are constant
Figure 13.7
At constant pressure...
Piston free to move
Relationship Between
Number of Gas Particles
and Volume
Increased number of gas
particles leads to increased
Gas added
Increased volume
volume if the temperature
and pressure are constant.
Constant
O
10
bjeCtive
e
temperature
You can see an
Increased number of gas particles
animation that
demonstrates
Increased number of collisions with the walls
this relationship
Increased total force of collisions
at the textbook’s
Web site.
Initial increased in force per area - that is, in pressure
Inside pressure is greater than external pressure
Container expands
Increased volume
Decreased pressure until the inside pressure equals the external pressure
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4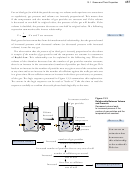 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10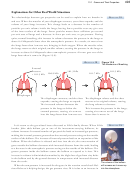 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25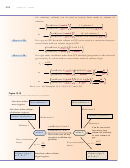 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








