Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 38
ADVERTISEMENT
520
Chapter 13
Gases
29. STP stands for “standard temperature and pressure.” Standard temperature is
_____________, or _____________, and standard pressure is _____________,
or _____________, or _____________.
30.
There are three different ways to convert between a measurable property and
moles in equation stoichiometry problems. For pure liquids and solids, we can
convert between mass and moles, using the _____________ as a conversion
factor. For solutions, _____________ provides a conversion factor that enables
us to convert between moles of solute and volume of solution.
31. The _____________ of the total pressure that one gas in a mixture of gases
contributes is called the partial pressure of the gas.
32.
Assuming ideal gas character, the partial pressure of any gas in a mixture is the
pressure that the gas would exert if it were _____________ in the container.
33. Dalton’s law of partial pressures states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases
is equal to the _____________ of the partial pressures of gas all the gases.
Chapter
Section 13.1 Gases and their Properties
Problems
34.
For a gas under typical conditions, what approximate percentage of the volume is
O
2
occupied by the gas particles themselves?
bjeCtive
35. One of the car maintenance tasks you might do at a service station is to fill your
tires with air. Why are the tires not really full when you get to the desired tire
pressure? Why can you still add more air to the tire?
36.
Why is it harder to walk through water than to walk through air?
37. What is the average distance traveled between collisions by molecules of oxygen
O
3
bjeCtive
gas, O
, at room temperature and pressure?
2
38.
What are the key assumptions that distinguish an ideal gas from a real gas?
O
4
bjeCtive
O
5
39. Consider a child’s helium-filled balloon. Describe the process that creates the gas
bjeCtive
pressure that keeps the balloon inflated.
40.
A TV weather person predicts a storm for the next day and refers to the dropping
barometric pressure to support the prediction. What causes the pressure in the
air?
41. What is the accepted SI unit for gas pressure? What is its abbreviation?
O
6, & 7
bjeCtives
The pressure at the center of the earth is 4 × 10
11
42.
pascals, Pa. What is this
O
8
bjeCtive
pressure in kPa, atm, mmHg, and torr?
43. The highest sustained pressure achieved in the laboratory is 1.5 × 10
7
kilopascals,
O
8
bjeCtive
kPa. What is this pressure in atm, mmHg, and torr?
44.
What does inversely proportional mean?
O
10
45. For each of the following pairs of gas properties, describe the relationship
bjeCtive
between the properties, describe a simple system that could be used to
demonstrate the relationship, and explain the reason for the relationship:
(a) volume and pressure when number of gas particles and temperature are
constant, (b) pressure and temperature when volume and the number of gas
particles are constant, (c) volume and temperature when pressure and the number
of gas particles are constant, (d) the number of gas particles and pressure when
volume and temperature are constant, and (e) the number of gas particles and
volume when pressure and temperature are constant.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4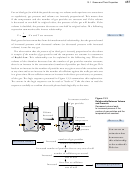 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10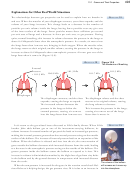 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28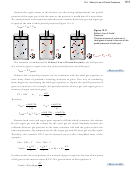 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








