Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 30
ADVERTISEMENT
512
Chapter 13
Gases
The following sample study sheet describes calculations that can be done using
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures.
Sample Study
T
-
– The problem involves a mixture of gases and no chemical reaction. You are
ip
off
asked to calculate a value for one of the variables in the equations below, and you are
Sheet 13.4
given (directly or indirectly) values for the other variables.
Using Dalton’s
G
S
- T
.
Law of Partial
eneral
TepS
he followinG STepS can be uSed To work TheSe problemS
Pressures
Step 1 Assign variables to the values that are given and the value that is unknown.
Step 2 From the following equations, choose the one that best fits the variables
O
21
bjeCtive
assigned in Step 1.
O
22
bjeCtive
RT
= ΣP
= (Σn
P
or
P
)
total
partial
total
each gas
V
Step 3 Rearrange the equation to solve for your unknown.
Step 4 Plug in the values for the given properties.
Step 5 Make sure that the equation yields the correct units. Make any necessary unit
conversions.
Step 6 Calculate your answer and report it with the correct units and with the correct
significant figures.
e
13.9 - Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
xample
A typical 100-watt light bulb contains a mixture of argon gas and nitrogen gas. In a
O
21
bjeCtive
light bulb with a total gas pressure of 111 kPa, enough argon is present to yield a partial
pressure of 102 kPa. What is the partial pressure of the nitrogen gas?
Solution
Step 1 Assign variables.
= 111 kPa
= 102 kPa
= ?
P
P
P
T
Ar
N
2
Step 2 Our variables fit the general equation
= S P
= P
+ P
P
or
P
total
partial
total
Ar
N
2
Steps 3-6 Solve the equation for the unknown variable, plug in the given values,
check the units, and calculate the answer.
= P
- P
= 111 kPa - 102 kPa = 9 kPa
P
N
total
Ar
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4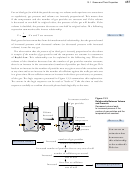 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10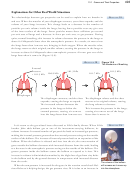 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25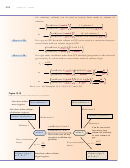 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








