Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
501
13.2 Ideal Gas Calculations
e
13.4 - Using the Combined Gas Law Equation
xample
Neon gas in luminous tubes radiates red light—the original “neon light.” The standard
O
18
bjeCtive
gas containers used to fill the tubes have a volume of 1.0 L and store neon gas at a
pressure of 101 kPa at 22 °C. A typical luminous neon tube contains enough neon
gas to exert a pressure of 1.3 kPa at 19 °C. If all the gas from a standard container
is allowed to expand until it exerts a pressure of 1.3 kPa at 19 °C, what will its final
volume be? If Lilia’s sister Amelia is adding this gas to luminous tubes that have an
average volume of 500 mL, what is the approximate number of tubes she can fill?
Neon tubes
Solution
We recognize this as a combined gas law problem because it requires calculating a value
for a gas property that has changed. In this case, that property is volume.
Step 1 We assign variables to the given values and to the unknown.
= 1.0 L
= 101 kPa
= 22 °C + 273.15 = 295 K
V
P
T
1
1
1
= ?
= 1.3 kPa
= 19 °C + 273.15 = 292 K
V
P
T
2
2
2
Step 2 We write the combined gas law equation, eliminating variables for properties
that are constant. Because moles of gas are not mentioned, we assume that
= n
they are constant (n
).
1
2
P
V
P
V
P
V
P
V
1
1
2
2
1
1
2
2
=
=
becomes
n
T
n
T
T
T
1
1
2
2
1
2
Steps 3 and 4 We rearrange the equation to solve for our unknown and plug in the
given values.
292 K
101 kPa
T
P
2
1
V
= V
= 1.0 L
2
1
295 K
1.3 kPa
T
P
1
2
Step 5 Our units cancel to yield liters, which is a reasonable volume unit, so we do
not need to make any unit conversions.
Step 6 We finish the problem by calculating our answer and reporting it with the
correct significant figures.
292 K
101 kPa
T
P
2
1
= 77 L
V
= V
= 1.0 L
2
1
295 K
1.3 kPa
T
P
1
2
We can now answer Amelia’s question about how many neon tubes she can expect to
fill from each neon cylinder.
3
10
mL
1 tube
2
= 1.5 × 10
? tubes = 77 L
tubes, or about 150 tubes
1 L
500 mL
Let’s look at another gas-related issue that Lilia’s sister Rebecca needs to consider in
designing the pressure valve for the reaction vessel at her chemical plant. She knows
that, for safety reasons, the overall pressure must be kept below 1000 kPa, and she
knows that the most likely cause of increased pressure is increased temperature. To
get an idea of how high the temperature can go safely, she could use the combined gas
law equation to calculate the temperature at which the pressure of the gas will reach
1000 kPa if the initial temperature was 825 °C (1098 K) and the initial pressure was
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4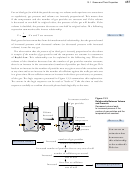 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28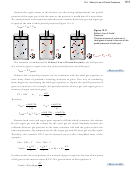 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








