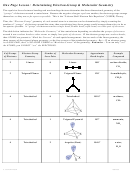
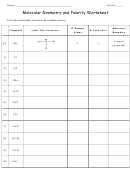
Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function Page 18
ADVERTISEMENT
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
– The shape predicted by VSEPR does not match the bond angles given by pure s and pure p
orbitals
atomic orbitals involved in bonding must be a combination of s and p orbitals
→
– To hybridize, mix s and p orbitals to get the same number of new hybridized orbitals
(e.g. mix one s and one p
two sp orbitals)
→
hybridization: mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom (usually central atom) to generate a
new set of atomic orbitals, called hybrid orbitals
sp Hybridization: mixing one s orbital and one p orbital
two sp orbitals
→
hybridize a 2s and a 2p orbital to get 2 equivalent sp hybrid orbitals:
→
______ ______ ______
______ ______
E
2p
______ ______
2p
______
sp
sp
2s
atomic orbital diagram before hybridizing
atomic orbital diagram after hybridizing
The two sp orbitals in Be are oriented along a line to maximize the
distance between electrons.
linear shape (180˚ bond angle) corresponding to
→
a form a linear molecule when the H atoms are bonded to the
Be atom.
Example: Sketch the BeH
molecule below by showing the Be
2
atom with sp orbitals, the H atoms with s orbitals, & bonds as
overlapping areas.
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
1 8
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5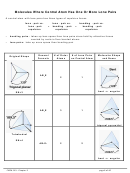 6
6 7
7 8
8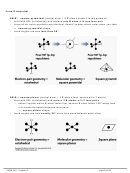 9
9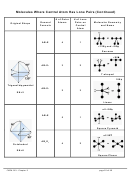 10
10 11
11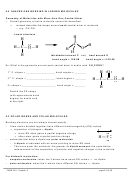 12
12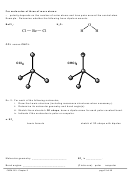 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19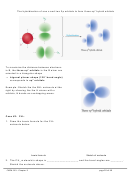 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33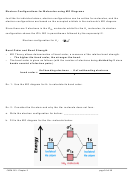 34
34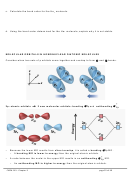 35
35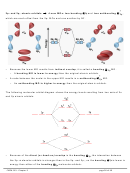 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40