Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function Page 28
ADVERTISEMENT
9.5 SHAPES AND BONDING IN LARGER MOLECULES
Double Bond Case: ethylene, C
H
:
2
4
1. Draw the Lewis structure for C
H
using the skeletal structure below:
2
4
H
H
C
C
H
H
2. The shape around each C is ____________________, and the bond angle is _________.
3. Electron configuration for C (using core notation): ___________________
4. Draw the atomic orbital diagram
for the valence electrons in C, promoting
electrons in the atomic orbital diagram,
so C can form 4 bonds.
5. Given the shape around each C atom, C has _______ atomic hybrid orbitals.
6. Show the atomic orbital diagrams forming the three hybrid orbitals for each C atom below:
hybridization
"
" " " " "
→
atomic orbital diagram before hybridizing
atomic orbital diagram after hybridizing
€
sigma (σ) bonds:
– covalent bond formed by directly overlapping orbitals
– for example, all of the bonds we’ve seen between the hybrid orbitals on the central atom
and the outer atoms’ orbitals have all been sigma bonds
– The electron density is concentrated between the two nuclei of bonding atoms.
– single bonds are generally sigma bonds
– only the first bond in double and triple bonds can be a sigma bond
pi (π) bond: (usually second and third bonds in double and triple bonds)
– covalent bond formed by sideways interaction between adjacent orbitals
– electron density concentrated above and below plane of the nuclei of bonding atoms
Example: Indicate the sigma and pi bonds in the ethylene molecule below:
H
H
_____ σ bonds
C
C
H
H
_____ π bonds
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
2 8
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5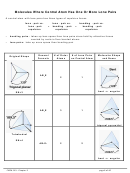 6
6 7
7 8
8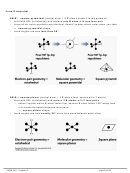 9
9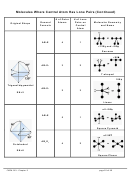 10
10 11
11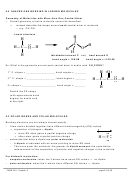 12
12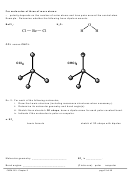 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19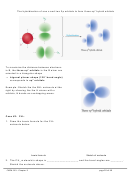 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33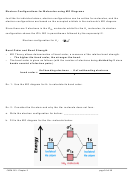 34
34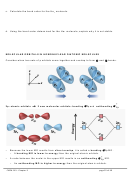 35
35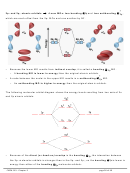 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40