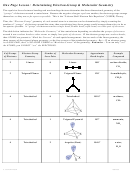
Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function Page 25
ADVERTISEMENT
To maximize the distance between
3
2
electrons in S, the five sp
d
orbitals in
the S atom are oriented as follows:
→ octahedral shape
(with 90˚ bond angles)
→ to get octahedral shape (or
variations like square pyramid
3
2
or square planar) must have sp
d
orbitals
Predicting what hybrid orbitals form on central atom of molecules:
1. Draw Lewis structure to determine total number of bonds on central atom
2. Given the shape of molecule or bond angle from the VSEPR model, we can determine
what hybrid orbitals must be involved:
Hybrid
Molecular Geometry (Shape)
Steric #
Orbitals
linear (e.g. HCN, BeCl
, CO
), central atom has 2 or 4 electron pairs
2
sp
2
2
2
3
sp
trigonal planar (120˚ bond angle or 120˚∠), bent (<120˚ ∠)
3
4
sp
tetrahedral (109.5˚ ∠), trigonal pyramid, or bent (<109.5˚ ∠)
3
5
sp
d
trigonal bipyramidal, see-saw, T-shape, linear (with expanded
octet/more than 4 electron pairs on central atom)
3
2
6
sp
d
octahedral or square planar (90˚∠), square pyramid (<90˚∠)
Example:
For each of the molecules on the following page,
i. Draw the Lewis structure.
ii. Use VSEPR to determine the molecule’s shape and bond angles,
iii. Draw atomic orbital diagrams for valence electrons before and after
hybridization.
iv. Indicate the atomic hybrid orbital for the central atom in each.
v. Sketch the molecule showing the hybrid atomic orbitals on the central atom
and hybrid or unhybridized orbitals on the outer atoms.
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
2 5
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8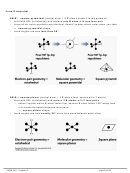 9
9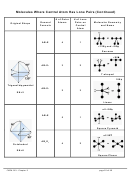 10
10 11
11 12
12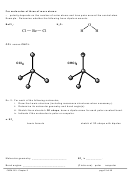 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19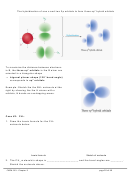 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33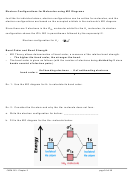 34
34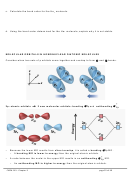 35
35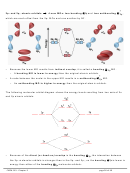 36
36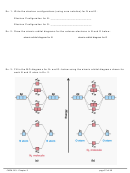 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40