Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function Page 29
ADVERTISEMENT
Each C–H bond and the first C–C bond all have a region of direct overlap where the shared
electrons are located—these are all sigma (σ) bonds, as shown below:
Note: The atomic orbital diagram for each C atom drawn in step 6 C shows an unhybridized p
orbital. The second C–C bond forms from the two electrons in the unhybridized p orbitals.
2
– Each C atom has an unpaired electron in the 2p
orbital, which is perpendicular to the sp
z
orbitals forming the C–H and first C–C bond.
– These two electrons in the 2p
bond via a sideways overlap as shown above.
z
Note: The carbon-carbon double bond in C
H
is made up of the following:
2
4
The σ bond is the first C–C bond, and the two lobes above and below (indicated as π
bond) together make up the π bond, which is the second C–C bond.
Triple Bond Case: C
H
:
2
2
1. Draw the Lewis structure for C
H
using the skeletal structure below:
2
2
_____ σ bonds
H
C
C
H
_____ π bonds
2. The shape around each C is ____________________, and the bond angle is __________.
3. Electron configuration for C (using core notation): ___________________
4. Given the shape around each C atom, C has _________ atomic hybrid orbitals.
5. Draw the atomic orbital diagram for
the valence electrons in C, promoting
electrons, so C can form 4 bonds.
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
2 9
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5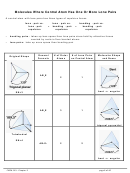 6
6 7
7 8
8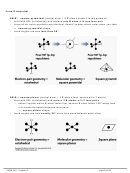 9
9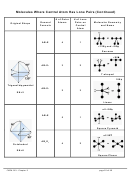 10
10 11
11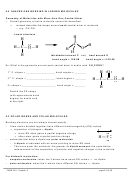 12
12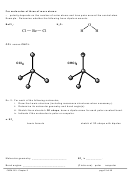 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19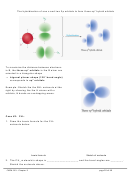 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33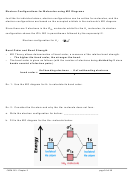 34
34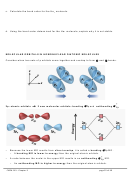 35
35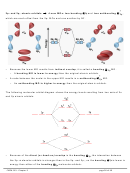 36
36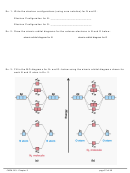 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40