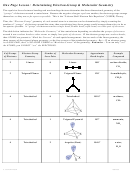
Chem 161 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Worksheet - Shape Determines Function Page 23
ADVERTISEMENT
4. Draw the atomic orbital diagram
for the valence electrons in P:
5. Promote electrons to 3d in the atomic orbital diagram, so P can form 5 bonds.
Although P now has unpaired electrons in 5 orbitals for bonding, the atomic orbital diagram
in step 5 above indicates that three of the P–F bonds (from 3p) should be the same, but two
(one from 3s and one from 3d) should be different.
But VSEPR predicts PF
is trigonal bipyramidal and experimental evidence indicates that the
5
five P–F bonds are equivalent
3
hybridize one 3s, three 3p orbitals, and one 3d orbital to get 5 equivalent sp
d hybrid
→
orbitals
Show the atomic orbital diagrams for the hybridization below:
hybridization
"
" " " " "
→
€
atomic orbital diagram before hybridizing
atomic orbital diagram after hybridizing
–
To maximize the distance between e
’s in
3
P, the five sp
d orbitals in the P atom are
oriented as shown at the right
→ trigonal bipyramidal shape
(with 120˚ and 90˚ bond angles)
→ to get trigonal bipyramidal
shape (or variations like see-saw, T-
3
shaped, etc.), must have sp
d orbitals
Case #5: SF
:
6
CHEM
1 61:
C hapter
9
page
2 3
o f
4 0
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5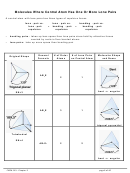 6
6 7
7 8
8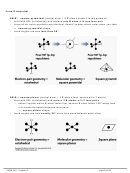 9
9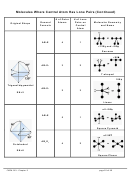 10
10 11
11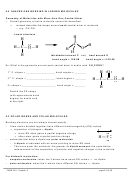 12
12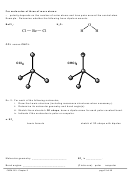 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19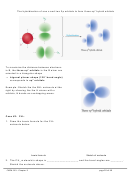 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33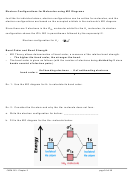 34
34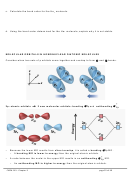 35
35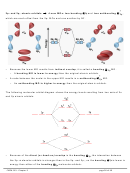 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40