Multi-Year Analysis Plan Page 10
ADVERTISEMENT
2
Role of Analysis in the Biomass Program
Analysis gives the Biomass Program context and justification for decisions at all levels by
providing quantitative metrics. From the macroscopic benefits analysis that shows yearly progress
toward DOE and EERE goals to the microscopic technical analysis that directs R&D projects on
a daily basis, analysis quantifies goals, targets, and results and provides alternative directions.
Analysis plays three main roles in the program:
1. It shows progress toward the goals of DOE/EERE/OBP via benefits analysis.
2. It provides direction and guidance for program planning functions.
3. It provides engineering knowledge for biorefinery development.
Analysis that contributes information in one or more of these areas is necessary for the program’s
success.
2.1 Shows Progress to the Goals of DOE/EERE/OBP via Benefits Analysis
Under DOE’s outcome based management system, research projects are selected by their
potential to improve society. The benefits or end outcomes of research need to be quantified so
that different projects can be compared and the comparisons used in portfolio management and
justification. Intermediate outcomes are the individual market effects of EERE research projects
and are necessary to calculate end outcomes. To communicate the necessary outcome
measurements, a framework was developed by EERE that shows the benefits of research. The
work proposed by this plan follows that evaluation framework.
The framework focuses on the benefits (also referred to as end outcomes or outcomes) already
achieved through the program’s work as well as potential benefits of the work on the expected
future scenario and a couple of potential future scenarios. Benefits are broken into the following
four categories: economic, environmental, security, and knowledge.
The framework was originally developed during a National Academy of Sciences (NAS) review
and published in the report titled “Energy Research at DOE: Was it Worth it? Energy Efficiency
2
and Fossil Energy Research 1978 to 2000.
” A modified version of the framework was included
in the GPRA data call (Performance Planning Guidance). The most recent version is shown in
Table 2 with prioritized evaluation areas; columns represent timeframes for the analysis and rows
represent criteria categories.
Table 2: Evaluation Framework with Prioritized Evaluation Areas
(H is high priority; M, medium priority; and L, low priority)
Realized
Expected Prospective
Option
Retrospective
Economic
L
H
M
Environmental
L
H
M
Security
L
H
M
Knowledge
L
EERE’s office of Planning, Budget and Analysis (PBA) is currently in the process of determining
which end outcomes will be used for selection and reporting. Different technologies address
2
National Research Council. “Energy Research at DOE Was it Worth it? Energy Efficiency and Fossil
Research 1978 to 2000.” National Academy Press, Washington, DC. (2001).
6
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16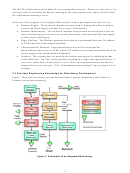 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32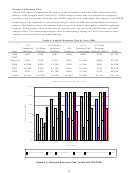 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49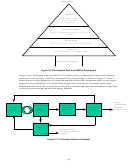 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75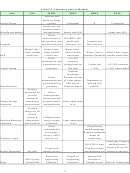 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80








